The Water Cycle: Part 1 - Oceans and Atmosphere
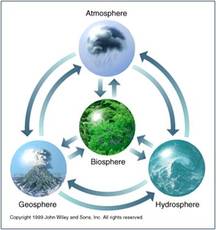
How does water travel from one sphere to the next?
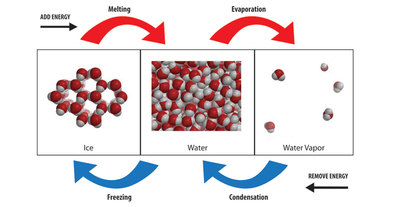
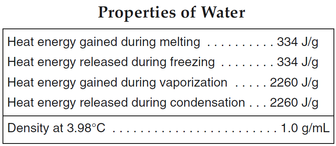
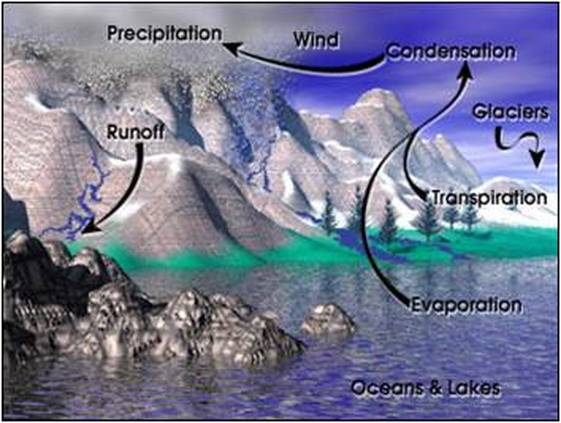
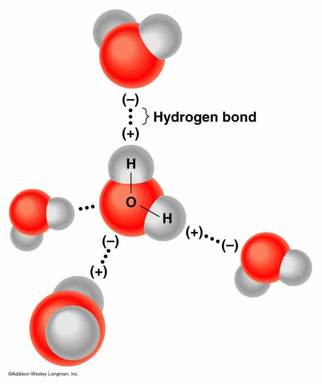
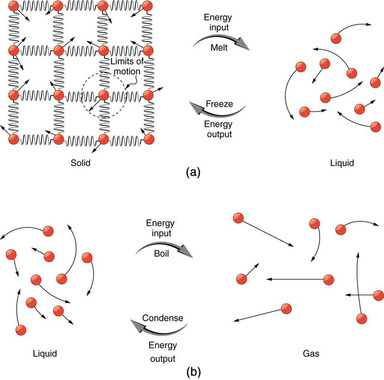
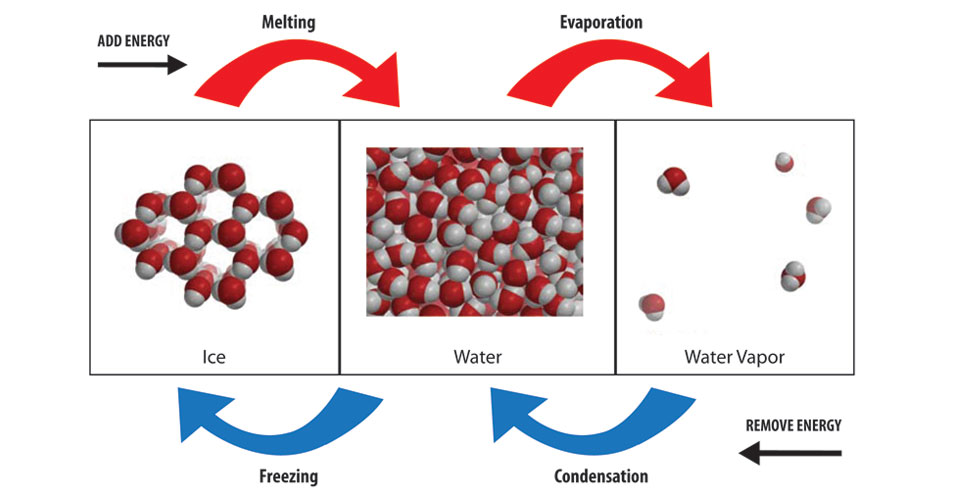
Basic Components:Evaporation: Occurs when liquid water gains enough energy from the sun and/or wind to change state into a gas.
Transpiration: Is the process in which plants release water vapor into the air. Evapo-Transpiration: Is the total amount of water vapor released into the air by land and plant life. Condensation: The process of water vapor releasing energy to change phase into liquid. Precipitation: The process of falling out.
Runoff: Water that does not sink into the ground and flows along the surface. |
|
Key Terms and Processes
The Dew Point and Cloud Formation
|
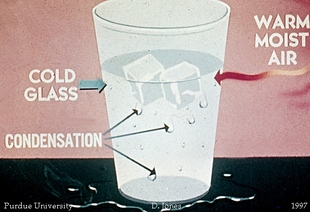
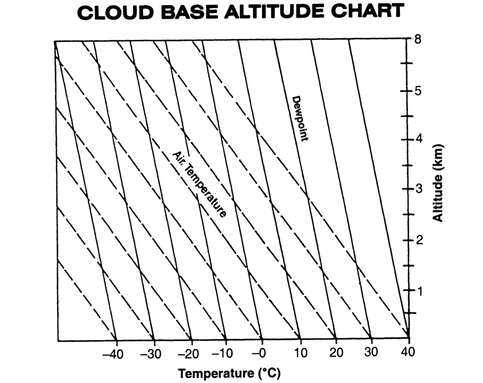
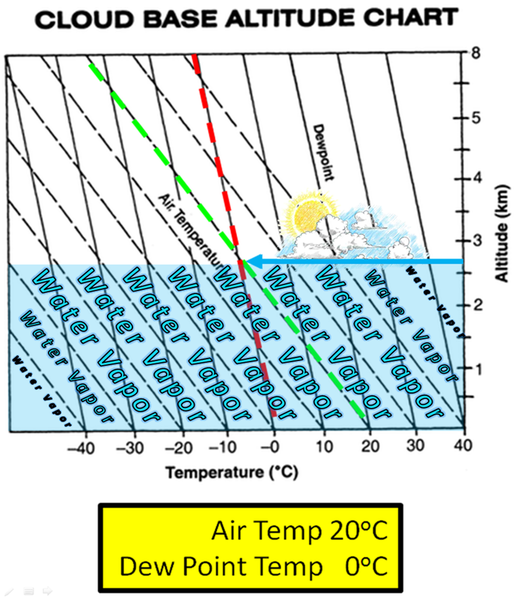
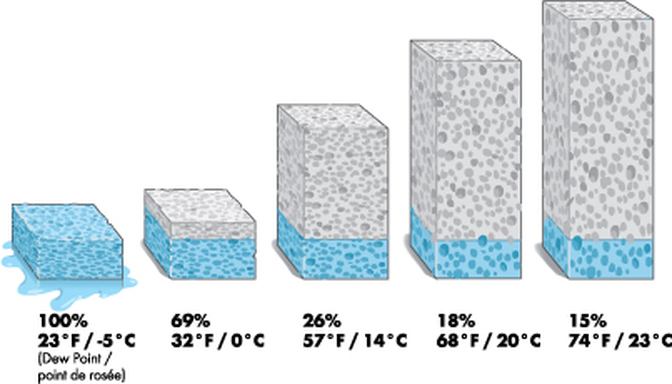
The dew point is the temperature to which the air has to cool in order for condensation to occur. You have probably seen this transformation occur on a glass containing ice water. The glass cools to the dew point temperature, and water vapor in the surrounding air condenses upon the glass. |
|
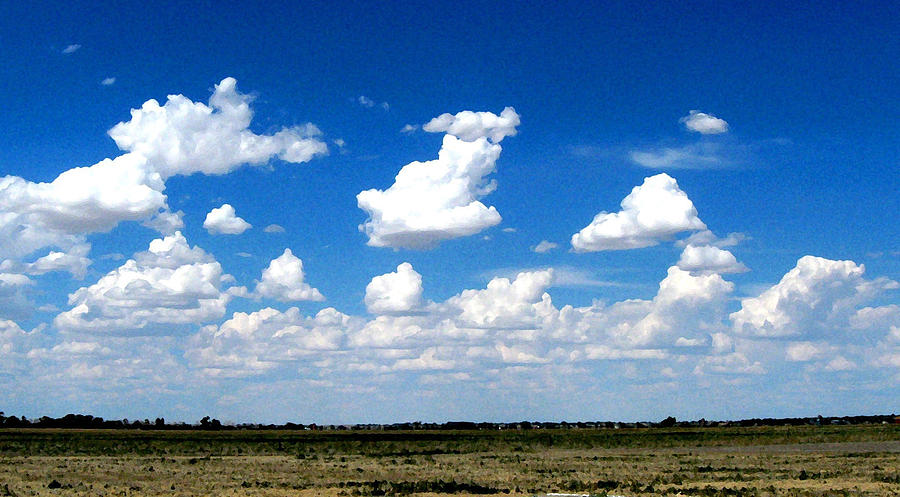
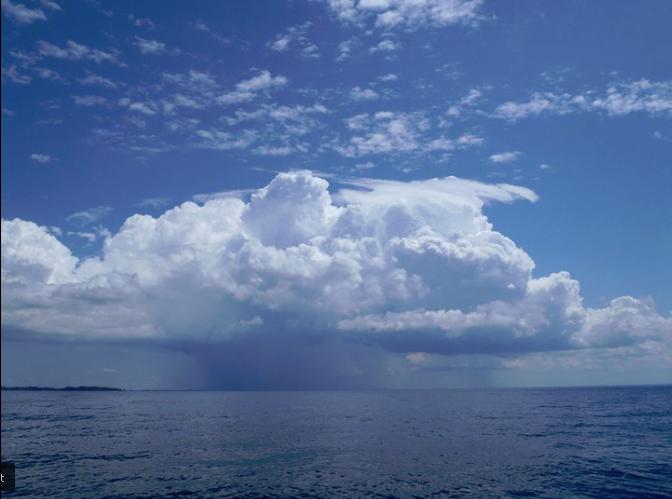
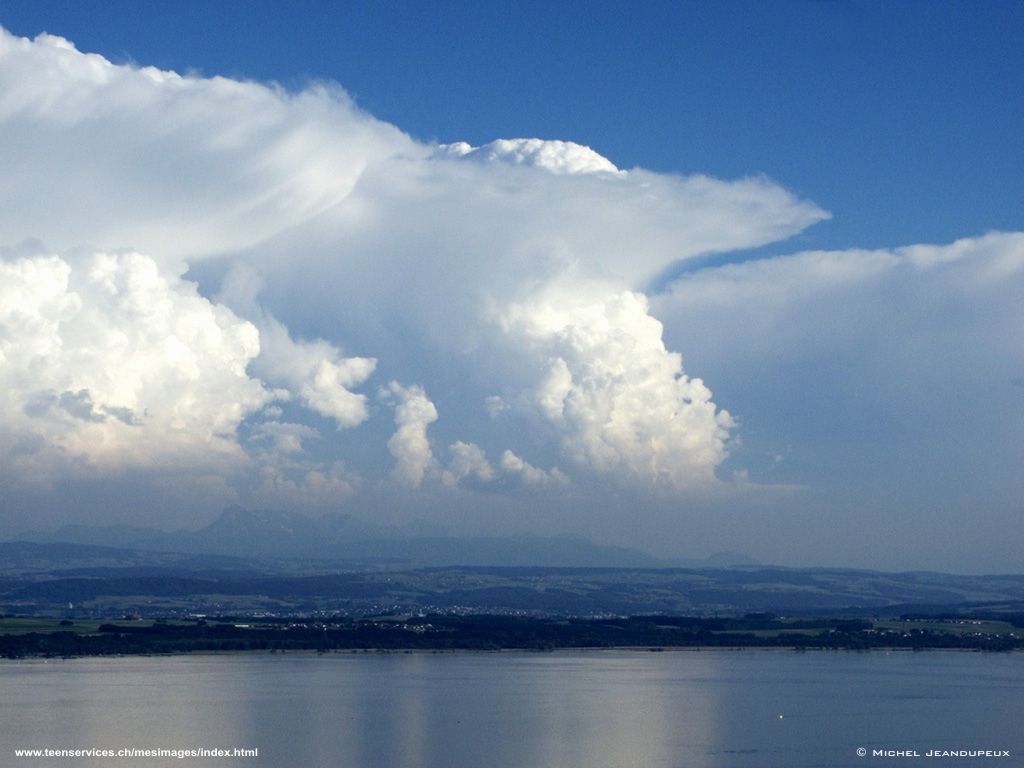
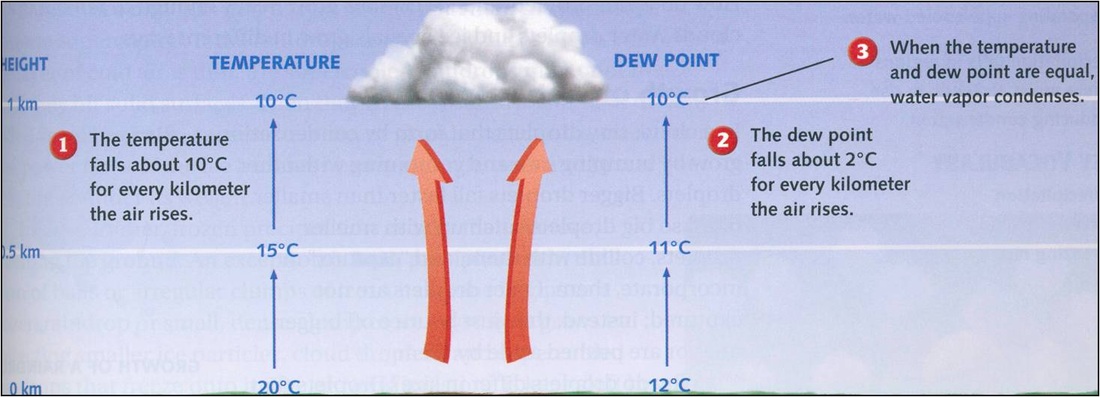
The closer the dew point temperature is to the actual temperature, the greater the chance of cloud formation and precipitation. The diagram below illustrates how clouds form in the atmosphere as air rises and cools to the dew point. |
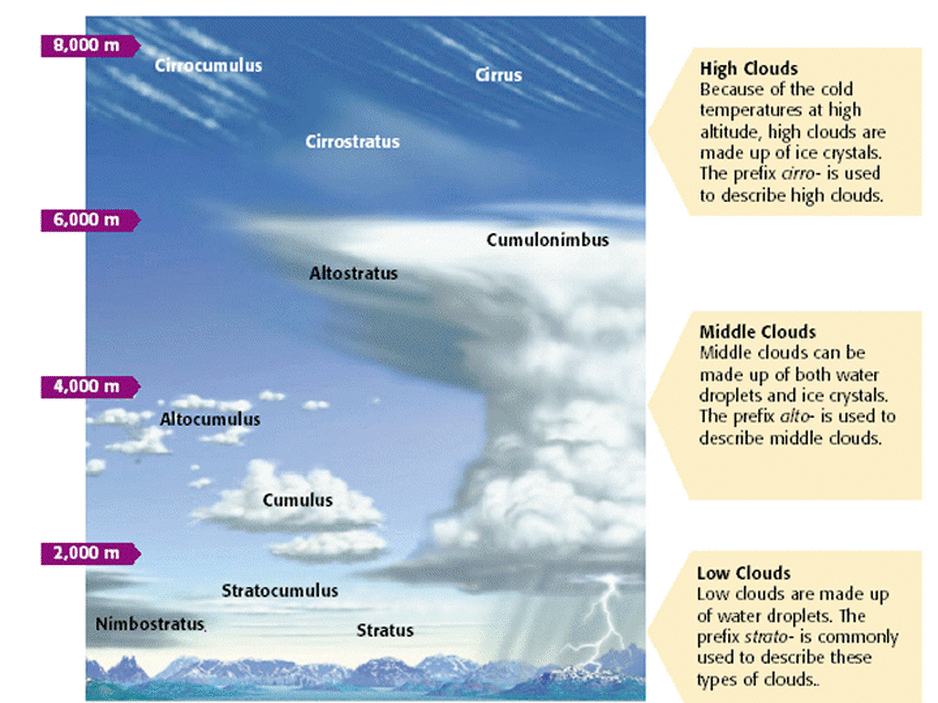
Cloud Formation
Clouds have flat bottoms because their bases are located at the elevation where the air has cooled to the dew point temperature.
|
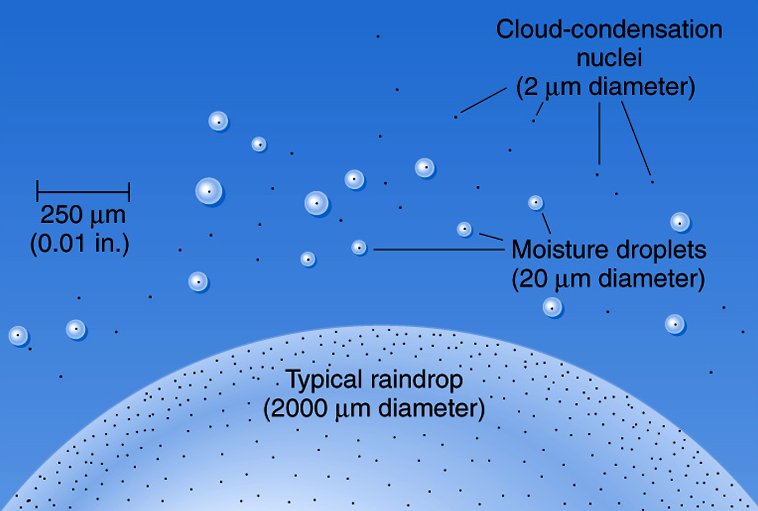
For condensation to occur, there needs to be a surface to adhere (stick) to called a Condensation Nuclei. Sea salt, dust, pollution, and pollen are all examples of particles that often end up as condensation nuclei. |
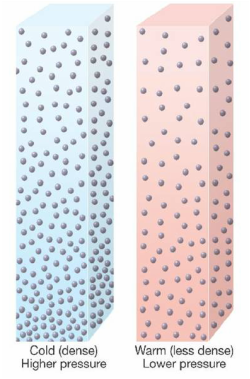
Absolute HumidityAbsolute humidity is the measurement of the exact amount of grams (g) of water vapor there are in a cubic meter of air.
|
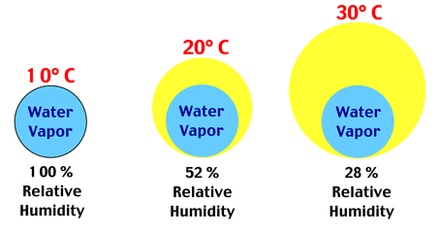
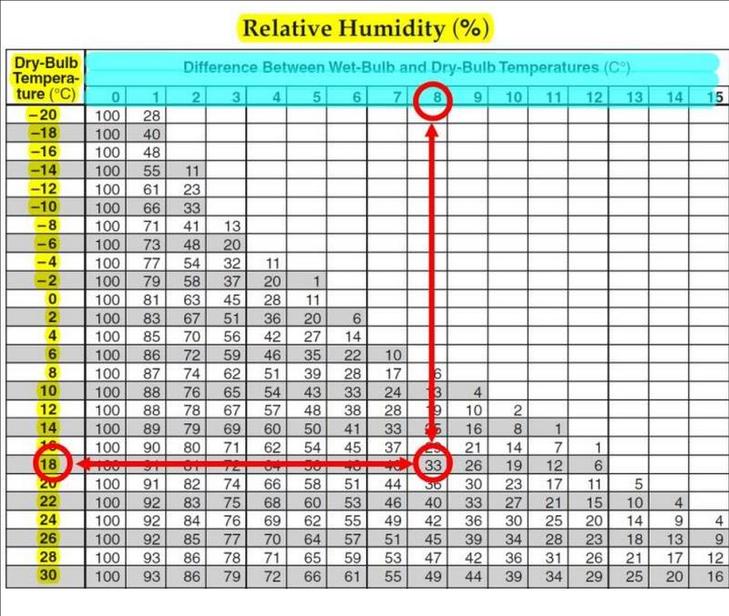
Relative HumidityRelative humidity is a comparison of the amount of water vapor in the air, relative to what it can hold at that temperature.
|
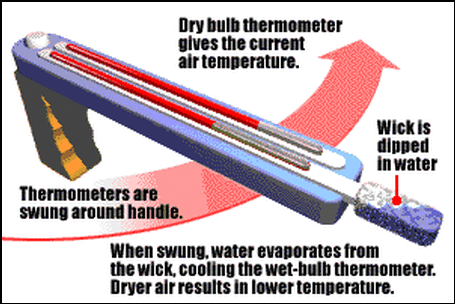
Instrument:Sling Psychrometer
|
Components & Measurements
|
Dew Point, Relative Humidity, & Cloud Formation Summary
As the air rises, it expands and cools to the dew point, allowing clouds to form. Precipitation occurs when the updrafts are not strong enough to support the weight of the condensed molecule.
As air cools, it contracts and water vapor is squeezed out of the space it had been in. You could think of the dew point as the temperature that, when the air cools it, there is no more room between air molecules for water vapor. It is filled to capacity. It is saturated, reached 100% relative humidity, and condensed droplets of dew form... as long as there are condensation nuclei available.
As air cools, it contracts and water vapor is squeezed out of the space it had been in. You could think of the dew point as the temperature that, when the air cools it, there is no more room between air molecules for water vapor. It is filled to capacity. It is saturated, reached 100% relative humidity, and condensed droplets of dew form... as long as there are condensation nuclei available.